Explore the Science Behind Coenzyme Q10:
Nature’s Energy-Driving Molecule

What is Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), also known as ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring compound found in almost every cell of the human body. It plays a fundamental role in energy production, acting as a key component in the biochemical chain that fuels life at the cellular level.
In this educational hub, explore how CoQ10 functions within mitochondria, supports energy metabolism, and inspires innovative research in molecular biology and biotechnology.
Coenzyme Q10
The Biochemical Overview
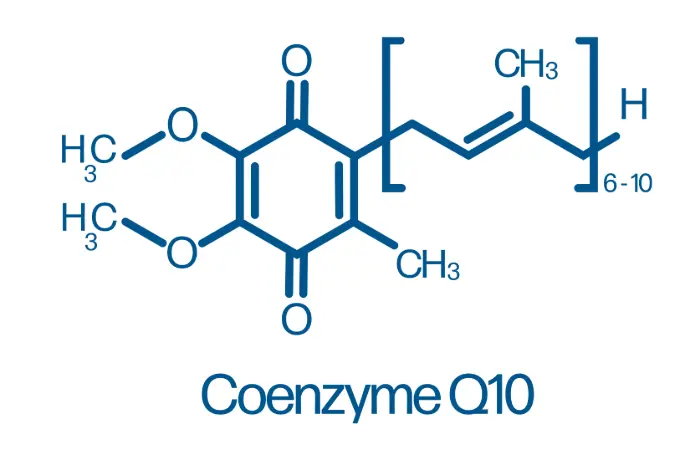
Biochemical overview
Coenzyme Q10 is a lipid-soluble quinone compound that serves as an essential electron carrier in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. It bridges the transfer of electrons between complexes I and II to complex III, a process that is central to cellular respiration and ATP synthesis.
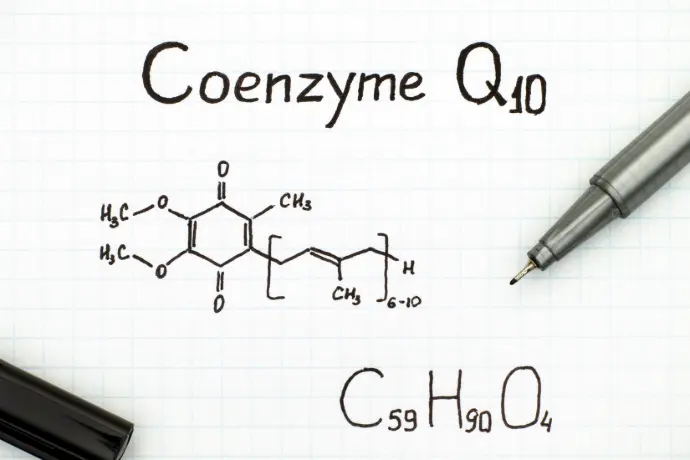
Structurally, CoQ10 contains a benzoquinone ring and a polyisoprenoid side chain, giving it unique redox properties. This molecule is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it acts as a dynamic shuttle for energy flow.

CoQ10 in Research and Biotechnology
In the world of biotechnology and molecular biology, CoQ10 has become a molecule of great scientific interest. It serves as a model compound in studies related to oxidative stress, mitochondrial disorders, and bioenergetic regulation.
Researchers use CoQ10 in laboratory assays that explore redox activity, antioxidant defense mechanisms, and the stability of mitochondrial function under experimental conditions. Moreover, advancements in enzymology and bioengineering continue to improve its extraction, purification, and application.
The Role of CoQ10 in Cellular Protection
Beyond its energetic role, CoQ10 acts as a powerful antioxidant within the mitochondrial membrane. By accepting and donating electrons, it helps neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA.
This protective function contributes to maintaining oxidative balance and preventing cellular stress. The molecule’s dual function energy carrier and antioxidant makes it a central player in maintaining molecular stability and cell homeostasis.
CoQ10 and Aging: A Molecular Perspective
From a molecular biology viewpoint, aging is associated with a gradual decline in mitochondrial efficiency and oxidative balance. Scientific studies have shown that CoQ10 levels tend to decrease with age, influencing bioenergetic performance at the cellular level.
This section explores the molecular connections between CoQ10, mitochondrial activity, and aging processes—without medical claims—highlighting how maintaining efficient redox reactions supports the vitality of cells throughout life.


Educational Resources and References
To learn more about the molecular science of CoQ10, explore academic databases, scientific journals, and educational materials in the fields of biochemistry, molecular biology, and biotechnology.
This platform aims to support continuous learning, offering insights into emerging research, biochemical principles, and laboratory methods related to Coenzyme Q10 and cellular energy systems.